Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism, essential for healing injuries and fighting infections. However, chronic inflammation, which persists without a clear cause, can damage healthy cells and lead to diseases like diabetes and heart problems. Diet plays a crucial role in controlling inflammation, and consuming anti-inflammatory foods can promote better health.

Understanding Inflammation
Before diving into specific foods, it’s important to grasp what inflammation is and why it matters. Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism. When you sustain an injury or contract an infection, your immune system responds by sending inflammatory cells to the affected area to repair tissue and fend off pathogens. This process is known as acute inflammation and is both necessary and beneficial for healing.
However, chronic inflammation is a prolonged, low-grade response that can occur even without a clear cause. Over time, this persistent inflammation can damage healthy cells and tissues, contributing to the development of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular problems, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions. Diet plays a significant role in regulating inflammation, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can help tip the balance toward better health.
The Role of Diet in Combating Inflammation
What we eat directly influences the chemical processes in our bodies. For example, diets rich in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can trigger and exacerbate inflammatory responses. On the other hand, foods packed with antioxidants, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals help neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and lower inflammation. Therefore, embracing an anti-inflammatory diet is a proactive way to support the immune system and promote overall wellness.
Top 5 Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Here are the top five foods that can help combat chronic inflammation, each offering unique benefits and nutrients:
1. Fatty Fish: The Omega-3 Rich Super food
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are among the most potent anti-inflammatory foods available. They are high in omega-3 fatty acids—specifically eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
How Fatty Fish Helps Fight Inflammation
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats play a critical role in reducing the production of inflammatory chemicals in the body. Regular consumption of omega-3s has been linked to lower levels of inflammatory markers.
- Heart and Brain Health: In addition to combating inflammation, omega-3s support cardiovascular health by reducing blood pressure and triglycerides. They are also vital for brain function and may help ward off neuro degenerative diseases.
Ways to Incorporate Fatty Fish
- Salads: Add flaked fish to your greens for a protein boost.
- Grilled or Baked: Enjoy salmon or trout with a drizzle of lemon and a side of roasted vegetables.
- Fish Tacos: Use grilled mackerel or sardines in tacos with fresh salsa and avocado.
2. Leafy Greens: Nature’s Nutrient Powerhouses
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and collard greens are bursting with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are essential in reducing inflammation.
Nutrients That Make Leafy Greens Effective
- Vitamins and Minerals: Rich in vitamins A, C, and K, leafy greens support immune function and help regulate inflammatory responses.
- Antioxidants: Compounds such as beta-carotene and combat oxidative stress, which is a significant driver of chronic inflammation.
- Fiber: The high fiber content promotes digestive health, which is linked to reduced systemic inflammation.
Delicious Ways to Enjoy Leafy Greens
- Stir-Fries: Add greens to stir-fries or soups to boost the nutritional profile of your meals.
- Smoothies: Blend kale or spinach with fruits and a splash of almond milk for a nutritious breakfast.
- Salads: Create vibrant salads by mixing various leafy greens with other vegetables, nuts, and a light olive oil dressing.
3. Berries: Small Fruits, Big Impact
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are small in size but mighty in their anti-inflammatory potential. They are renowned for their high levels of antioxidants and phyto chemicals.
The Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Berries
- Anthocyanins: These potent antioxidants give berries their vibrant colors and help neutralize free radicals, reducing inflammation.
- Fiber Content: The natural fiber in berries supports digestive health, which is crucial for maintaining a balanced immune response.
- Versatility: Berries are low in calories yet high in nutrients, making them a perfect snack or addition to various dishes.
How to Incorporate Berries Into Your Diet
- Desserts: Use berries to create healthy desserts, such as a berry compote or fruit salad.
- Breakfast: Sprinkle berries over oatmeal, yogurt, or cereal.
- Snacks: Enjoy a bowl of mixed berries as a refreshing mid-day snack.
4. Nuts and Seeds: Packed with Healthy Fats and Fiber
Nuts and seeds, including almonds, walnuts, seeds, and flax seeds, are nutritional gems loaded with healthy fats, fiber, and protein—all of which play a role in reducing inflammation.
Why Nuts and Seeds Are Beneficial
- Plant-Based Omega-3 s: Although not as rich as fish, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide alpha-lino lenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that helps fight inflammation.
- Antioxidants and Poly : These compounds help reduce oxidative stress and modulate inflammatory responses.
- Fiber: The high fiber content supports a healthy digestive tract, which is essential for overall immune function.
Creative Ways to Enjoy Nuts and Seeds
- Baking: Incorporate chopped nuts into your baked goods for extra texture and nutritional value.
- Snacks: Keep a small container of mixed nuts for a quick, nutrient-dense snack.
- Smoothie Boost: Add a tablespoon of chia seeds or flax seeds to your smoothies.
5. Olive Oil: The Golden Elixir
Extra virgin olive oil is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet and is widely celebrated for its potent anti-inflammatory properties. Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, olive oil is a versatile ingredient that can enhance both the flavor and health profile of your meals.
Key Components of Olive Oil
- Oleocanthal: This naturally occurring compound in extra virgin olive oil has anti-inflammatory properties similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Antioxidants: The polyphenols in olive oil help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative damage and inflammation.
- Heart Health: Regular use of olive oil can improve cholesterol levels and support cardiovascular function.
How to Use Olive Oil in Your Daily Diet
- Dipping: Enjoy a simple appetizer of olive oil with whole-grain bread and a sprinkle of herbs.
- Salad Dressings: Use olive oil as the base for homemade salad dressings.
- Cooking: Drizzle olive oil over steamed vegetables or use it for light sautering.
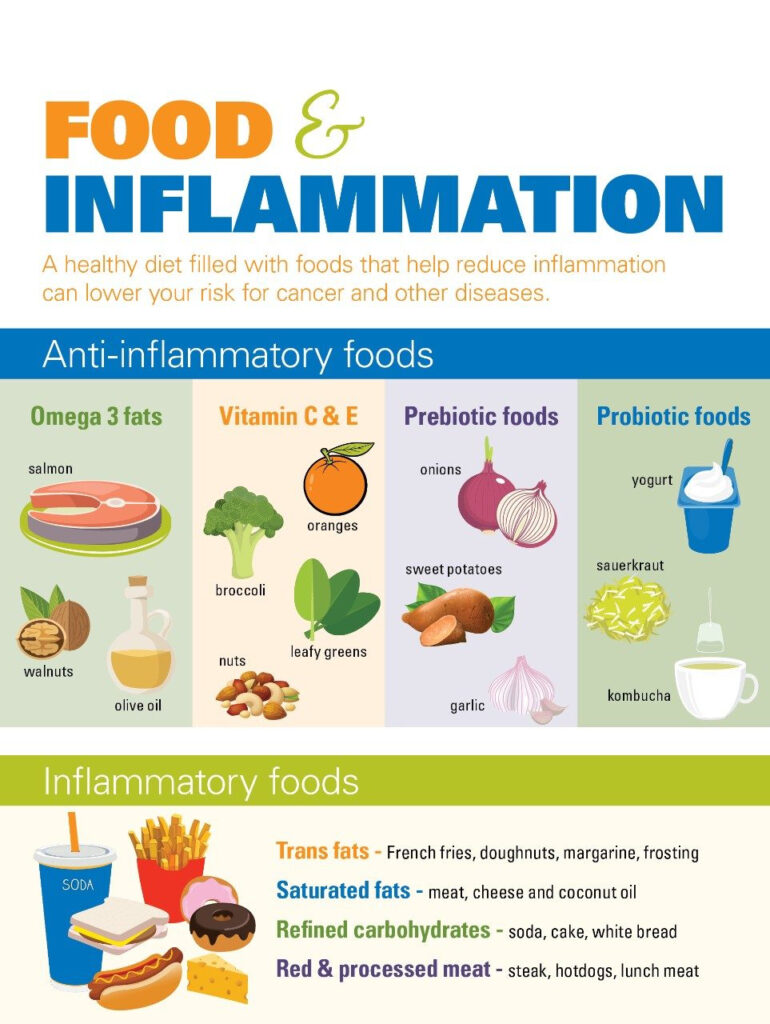
Additional Strategies for an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
While the five foods listed above are powerful tools in the fight against chronic inflammation, a comprehensive approach to health also includes other dietary and lifestyle strategies. Here are a few additional tips to consider:
- Stress Management: Chronic stress is a known contributor to inflammation. Therefore, incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can effectively help keep stress in check.
- Spices and Herbs: To further support an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, incorporate spices such as turmeric, ginger, and garlic into your cooking. Not only do these ingredients add flavor, but they also offer potent health benefits.
- Whole Grains and Legumes: Instead of refined grains, choose whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats. Additionally, legumes such as beans and lentils are excellent sources of protein and fiber, which help support a balanced diet.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health. In addition to aiding digestion, proper hydration helps the body remove toxins, which contributes to reduced inflammation.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise not only improves circulation but also helps reduce inflammation by lowering stress levels. As a result, engaging in physical activity consistently can significantly enhance overall well-being.
Tips for Embracing an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are some practical tips to help you transition smoothly:
- Within the Nuts and Seeds Section:
“Nuts and seeds are celebrated for their healthy fats, yet their anti-inflammatory benefits extend far beyond this. Furthermore, the antioxidants and poly present in these foods offer an extra layer of protection against oxidative stress.” - Plan Your Meals: Create a weekly meal plan that incorporates a variety of anti-inflammatory foods. Planning ahead helps you avoid impulse choices that may trigger inflammation.
- Experiment with Recipes: Explore new recipes that feature fatty fish, leafy greens, berries, nuts, and olive oil. This variety not only keeps your meals exciting but also ensures you receive a broad range of nutrients.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control ingredients and avoid processed additives. It’s also a great way to experiment with different flavors and textures.
- Mindful Eating: Take time to enjoy your meals. Eating slowly and savoring each bite can improve digestion and help you tune into your body’s needs.
- Stay Consistent: Small, consistent changes to your diet can lead to significant health improvements over time. Remember that progress is more important than perfection.
- Within the Fatty Fish Section:
Not only do fatty fish deliver essential omega-3 fatty acids, but they also contribute to overall cardiovascular health. Moreover, these nutrients work synergistically to combat inflammation at a cellular level. - Within the Leafy Greens Section:
Leafy greens offer more than just vitamins and minerals—they also provide vital antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals. In addition, their high fiber content plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy digestive system, further reducing inflammation.
True wealth is having your health and knowledge of self!
benjamin franklin
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation is a silent adversary that can gradually undermine your health over time. Fortunately, you have the power to combat it through your dietary choices. By consistently incorporating the top five anti-inflammatory foods—fatty fish, leafy greens, berries, nuts and seeds, and olive oil—into your daily routine, you can effectively reduce inflammation and ultimately support overall wellness. As a result, making these simple yet impactful changes can lead to long-term health benefits.


