When it comes to fitness, one of the most debated topics is whether strength training or cardio is the better choice. Both forms of exercise offer significant health benefits, but they serve different purposes. Strength training focuses on building muscle and increasing metabolic rate, while cardio enhances endurance and supports heart health. Understanding the unique benefits of each can help individuals tailor their workouts based on their fitness goals.

Understanding Strength Training and Cardio
What Is Strength Training?
Strength training, also known as resistance training, focuses on building muscle mass, endurance, and strength. It involves lifting weights, using resistance bands, or performing bodyweight exercises. The primary goal is to increase muscle hypertrophy, improve functional strength, and enhance metabolism.
What Is Cardio?
Cardiovascular exercise, commonly referred to as cardio, includes activities that elevate heart rate and improve endurance. Running, cycling, swimming, and brisk walking fall under this category. The key focus is to enhance heart health, improve oxygen consumption, and support weight management.
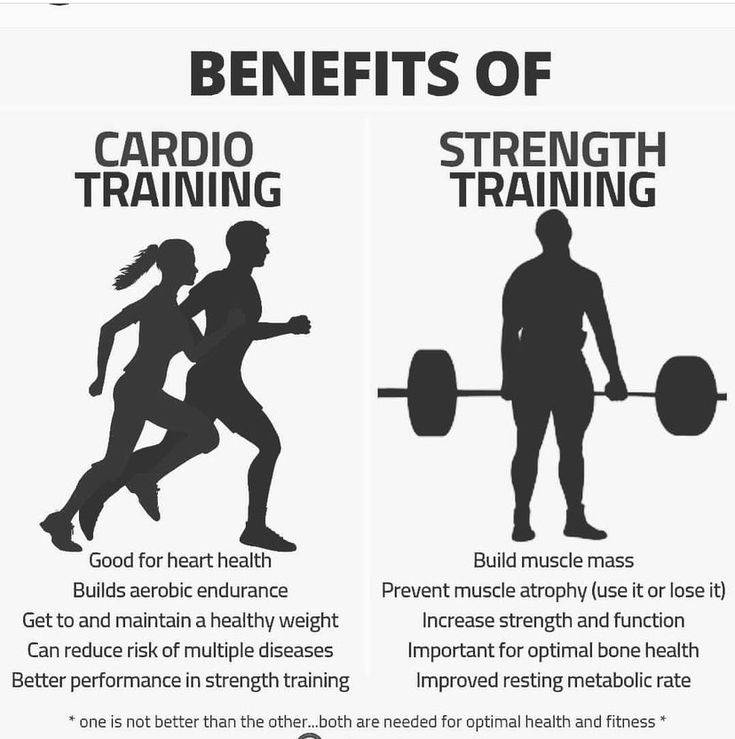
Benefits of Strength Training
Muscle Growth and Strength
Strength training increases muscle fiber size, leading to stronger and more defined muscles. Over time, progressive overload helps in enhancing muscular endurance and power.
Metabolic Boost
After a strength training session, the body continues to burn calories due to excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). This effect contributes to long-term fat loss.
Bone Density and Joint Health
Resistance training strengthens bones by increasing mineral density. It also enhances joint stability, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and injuries.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Strength training helps regulate blood sugar by increasing glucose uptake in muscles. This reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes and improves overall metabolic function.
Benefits of Cardio
Heart and Lung Health
Cardio workouts enhance cardiovascular efficiency by strengthening the heart and lungs. Over time, this leads to better circulation and oxygen distribution.
Weight Management
Regular cardiovascular activity burns calories effectively, making it a great tool for weight loss and maintenance.
Mood Enhancement and Stress Reduction
Aerobic exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. Activities like running or dancing can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Increased Endurance and Stamina
Engaging in cardio consistently improves stamina, making daily activities easier and reducing fatigue.
Strength Training vs. Cardio for Fat Loss
Which Burns More Calories?
Cardio burns more calories per session, especially high-intensity workouts like sprinting or jumping rope. However, strength training builds muscle, which increases resting metabolic rate, leading to long-term calorie burn.
Fat Loss vs. Weight Loss
Weight loss refers to overall body weight reduction, while fat loss specifically targets adipose tissue. Strength training preserves muscle mass while reducing fat, creating a leaner physique. Cardio helps burn fat efficiently but may also lead to muscle loss if overdone without proper nutrition.
Strength Training vs Cardio for Muscle Building
Strength training is the most effective way to build and maintain muscle. Cardio does not contribute significantly to muscle growth but can complement resistance training by improving recovery and circulation.
Strength Training vs Cardio for Heart Health
Both forms of exercise benefit heart health. However, aerobic exercises directly strengthen the heart and improve blood flow. Strength training contributes indirectly by reducing body fat and lowering blood pressure.
Combining Strength Training and Cardio
The Best of Both Worlds
Integrating strength and cardio workouts offers a balanced approach to fitness. A combination enhances endurance, muscle strength, and cardiovascular health.
Ideal Workout Routine
For optimal benefits, include strength training at least three times per week while engaging in cardio sessions on alternate days. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) can merge both for maximum efficiency.
Which One Is Right for You?
Goals and Preferences
Choosing between strength training and cardio depends on individual fitness goals. Those seeking muscle growth and strength should prioritize resistance exercises, while individuals focused on endurance and weight loss may benefit more from cardio.
For athletes or those training for specific sports, incorporating both is essential. Runners and cyclists need endurance-based cardio, while powerlifters and bodybuilders focus on resistance training. If the goal is overall health, a combination of both works best.
Age and Lifestyle Factors
Age, activity level, and health conditions also influence workout choices. Strength training becomes crucial as aging leads to muscle loss, while cardio remains essential for heart health.
For younger individuals, high-intensity workouts can maximize results. Older adults should focus on low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and light resistance exercises. Those with joint issues may find strength training with controlled movements more beneficial than high-impact cardio.
Time Constraints and Efficiency
If time is limited, strength training may provide more benefits in shorter sessions due to its metabolic impact. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) offers a time-efficient way to combine strength and cardio in a single workout.
Psychological and Emotional Considerations
Some people find cardio more enjoyable due to the rhythmic and repetitive nature of activities like running or cycling. Others prefer the progressive challenge of lifting weights. Enjoyment plays a key role in consistency, which ultimately determines long-term success.
Health Conditions and Risks
Individuals with heart conditions should, therefore, prioritize moderate-intensity cardio under medical supervision. Meanwhile, those with osteoporosis or arthritis can benefit more from strength training, as it helps improve bone density and joint function.
Furthermore, people recovering from injuries may require a customized plan that incorporates both forms of exercise with necessary modifications. Consequently, consulting a fitness professional or healthcare provider ensures a safe and effective approach.
Conclusion
Strength training and cardio each offer unique benefits. While strength training focuses on muscle growth and metabolic enhancement, cardio, on the other hand, improves cardiovascular function and endurance. Therefore, the best approach is to incorporate both based on personal goals, ensuring a well-rounded fitness routine. Moreover, by understanding the strengths of each, individuals can make informed choices for long-term health and fitness.


